NVMe Disk Vs SSD Disk
Computer storage devices are extremely significant. They store digital data as well as keep track of the media that is present in the device. It's built right into the computer's hardware. A computer's normal operation would be impossible without storage.
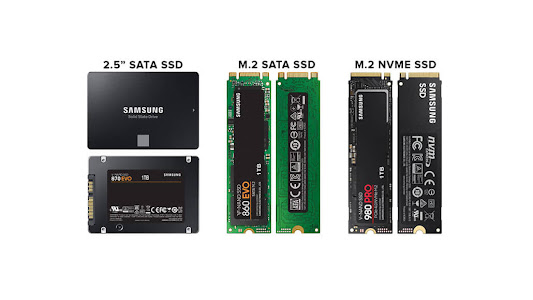
Solid-state drives (SSDs), whether traditional SATA or more advanced NVMe, are an essential component of any modern PC. Knowing the differences between these two types of SSDs is also crucial since they can have a significant impact on the cost, size, and performance of your system.
NVMe Disk
NVM express created the first NVMe interface. It began in 2011 and has now lasted ten years. After people encountered various problems with solid-state disks, they felt compelled to create the interface. NVMe must be physically attached to the storage media, much as SSDs.
NVMe, unlike SSDs, can perform multiple queries or commands at once. They can bring together the results of many inquiries and operations. This decreases latency and ensures that retrieving results is as quick as possible. They are 2.5" cards that fit into the computer's storage system.
In 2007, at the Intel Developer Forum, the first step toward accessing non-volatile memory was revealed.
By 2008, it was finished and posted on Intel's website. The NVMe requirements were developed by a group of over 90 firms. The NVMe was commercially accessible in August of 2012, thanks to Integrated Device Technology.
SSD Disk
SanDisk was the first company to introduce a solid-state drive. It's also known as a solid-state disk or solid-state device. It could only store 20 MB of data when it was initially released in 1991. These drives now have a storage capacity of 60-100 TB.
These drives are less susceptible to physical damage and are more shock-resistant. They have a fast access time and do not require the spinning of the disk to function. The number of bits in a single cell can affect the performance of various drives. Single-cell drives are the quickest and most durable, as well as the most cost-effective.
Early SSDs relied on RAM technology, however, this proved ineffective because, despite being fast, they lost data as soon as the power was turned off. As a result, information was lost. As a result, a more reliable technology was needed, and flash memory was chosen. The data held in the solid-state drive's flash memory was not lost when the power went out; rather, it was saved inside the device.
Their Difference Based on Different Factors
Performance
NVMe allows drivers to share a single lane "pool" that connects directly to the CPU. This allows for scalable performance by expanding beyond the standard four lanes found in most PCIe SSDs and putting them to use for execution. PCIe sockets can transport 25 times more data than SATA connectors.
Price
SSDs are priced differently based on their size and capacity. SSDs typically have capacities ranging from 120 GB to 2 TB and cost nearly four times as much as a comparable SATA disk. For really high-performance needs, NVMe may be the best enterprise alternative, but it is more expensive than SSDs.
Compatibility
NVMe corresponds directly with the CPU. It is compatible with all major operating systems, regardless of form factor. SSDs, on the other hand, are made for certain devices and are not compatible with other devices or operating systems.
Speed
When employing NVMe, which has a read/write throughput significantly higher than hard drives and SSDs, there is a distinct and demonstrable improvement in performance. SSDs are far slower than NVMe disks. On each route, PCIe 3.0, the current iteration of the PCI Express standard, offers a maximum speed transmission of 985 megabytes per second (Mbps). NVMe drives support up to four PCIe lanes, resulting in a theoretical maximum speed of 3.9 Gbps (3,940 Mbps).
Conclusion
While SSD is less expensive than NVMe, it is still widely used in older PCs. NVMe, on the other hand, is a new standard that provides great performance, low latency, and a large amount of storage space.
If you are looking for a storage solution that's faster and more responsive, you should look into the NVMe possibilities. Although it is costly, the investment is worthwhile. NVMe storage's dominance is expanding beyond just one application, thanks to breakthrough technologies like NVMe-oF (NVMe Over Fabrics) and Parallel I/O.
Over the last few years, storage has altered dramatically. NVMe takes performance to new heights and outperforms SATA by a wide margin. SSDs, on the other hand, are more energy-efficient, lighter, and faster. Which storage disk is best for you will be determined by your demands.


Comments
Post a Comment